
When light particles strike the solar cell, the photons present in the light will have enough energy to knock the electrons from their bond, leading it to move towards the N-side, and the hole (formed by the absence of an electron) will move towards the P-side. The N-type layer has excess electrons, and the p-type layer has extra holes. The top layer of the solar cell is doped with phosphorous to convert it into an n-type semiconductor, and the lower layer is doped with boron to convert it into a p-type semiconductor. These solar cells usually have two layers of semiconductors. By having these strong bonds, the electrons will stay in one place, and no current flow is seen. The silicon atoms in the solar cells form 4 strong bonds with its neighboring silicon atoms. Solar cells are usually made out of silicon wafers. We will see how a solar panel works and design a solar mobile phone charger circuit to charge our mobile phone as well as to protect the battery from overcharging. To convert solar energy into electricity, we will need solar panels. In today's project, we are going to use solar energy to charge our mobiles. There are different types of renewable energy sources like wind, tidal, solar, etc. One of the solutions to these kinds of problems is to depend on the renewal energy sources. It becomes a major concern when you are in a place where electricity is not available. They all face one problem, and that is the need to charge after regular usage. have become an important part of our life. 8.Gadgets like phones, iPods, smartwatches, etc.Mismatch for Cells Connected in Parallel.
#ICIRCUIT SOLAR PANEL SERIES#
The total voltage is the voltage of an individual cell multiplied but the number of cells in series. The total current is simply the current of an individual cell multiplied by the number of cells in parallel. The overall IV curve of a set of identical connected solar cells is shown below. N is the ideality factor of a single solar cell Īnd q, k, and T are constants as given in the constants page. I L is the short-circuit current from a single solar cell I 0 is the saturation current from a single solar cell V T is the total voltage from the circuit I T is the total current from the circuit In this case, the IV curve of the PV module has the same shape as that of the individual cells, except that the voltage and current are increased. If all the solar cells in a module have identical electrical characteristics, and they all experience the same insolation and temperature, then all the cells will be operating at exactly the same current and voltage. There are other sizes such as 96 cell modules but they are much less common. Modules for residential or large fields usually contain either 60 or 72 cells. I MP and I SC do not change that much but V MP and V OC scale with the number of cells in the module. The table below shows the output of typical modules at STC. Single crystal solar cells are often 15.6 × 15.6 cm 2, giving a total current of almost 9 – 10A from a module. At AM1.5 and under optimum tilt conditions, the current density from a commercial solar cell is approximately between 30 mA/cm 2 to 36 mA/cm 2.
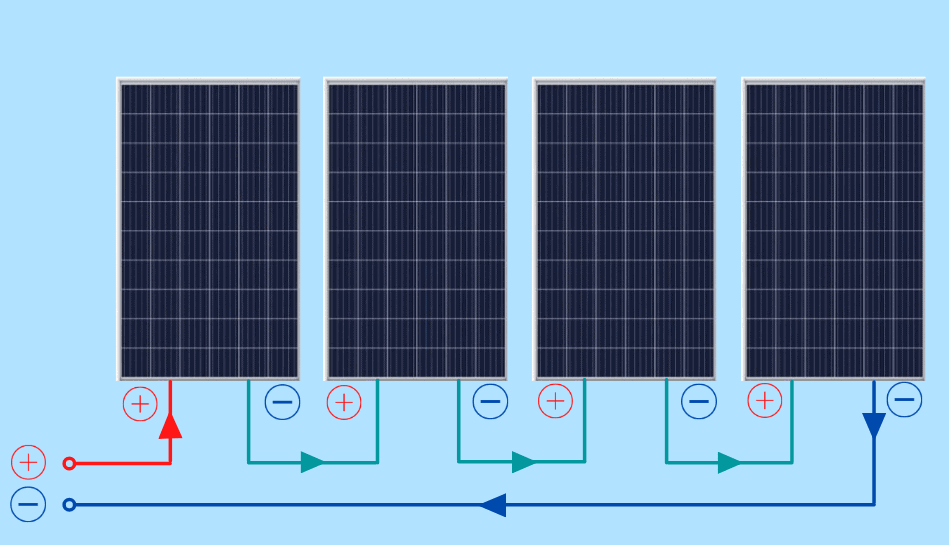
The voltage from the PV module is determined by the number of solar cells and the current from the module depends primarily on the size of the solar cells. In a typical module, 36 cells are connected in series to produce a voltage sufficient to charge a 12V battery. The remaining excess voltage is included to account for voltage drops caused by other elements of the PV system, including operation away from maximum power point and reductions in light intensity. This gives an open-circuit voltage of about 21V under standard test conditions, and an operating voltage at maximum power and operating temperature of about 17 or 18V. Taking into account an expected reduction in PV module voltage due to temperature and the fact that a battery may require voltages of 15V or more to charge, most modules contain 36 solar cells in series. An individual silicon solar cell has a voltage at the maximum power point around 0.5V under 25 ☌ and AM1.5 illumination. The voltage of a PV module is usually chosen to be compatible with a 12V battery. A bulk silicon PV module consists of multiple individual solar cells connected, nearly always in series, to increase the power and voltage above that from a single solar cell.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
